Sustainable waste management
Waste management goes beyond discarding garbage. It involves all the activities and processes required to handle waste material. These include collection, diversion, and disposal.
Sustainable waste management generates environmental, social, and economic benefits for all. By enforcing proper waste management practices, communities also contribute to sustainable development by achieving several SDGs.
Connecting resource and waste management to the UN SDGs
3: Good health and well-being

- Prevents hazardous waste from entering drinking water or affecting air quality
- Protects human health
12: Responsible consumption and production

- Improves resource efficiency
- Reduces waste during production
13: Climate action

- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions
14: Life below water

- Reduces solid waste runoff and accumulation of plastics in marine environments
- Reduces exposure to hazardous waste
15: Life on land

- Reduces presence of garbage and plastics on land
- Reduces land required for waste storage and processing
- Reduces exposure to hazardous waste
How do you achieve sustainable resource and waste management?
Waste diversion
The process of redirecting waste from the landfills. This can be achieved though composting organic waste or recycling inorganic waste to ensure minimal waste is incinerated at the landfills.
Waste management hierarchy
Since the rate of resource consumption and waste generation has increased over the years, it has become evident that human actions have had a negative impact on the environment, hence the need for better management.
Introduced by the European Commission in the 1970s, the waste management hierarchy is a framework designed to guide and rank waste management decisions at both the individual and organizational levels. In this hierarchy, waste prevention is the most environmentally friendly, while disposal is the least preferred option for waste management. This concept is more commonly known as the 3Rs: reduce, reuse, recycle.
However, there are five steps within the complete hierarchy. These steps have been adopted by UNB to ensure that more waste is diverted from the landfill than disposed of.
The 3 Rs vs. the 5 Rs
Let's look at the differences between the 3Rs and 5Rs in the waste management hierarchy.
The 3 Rs
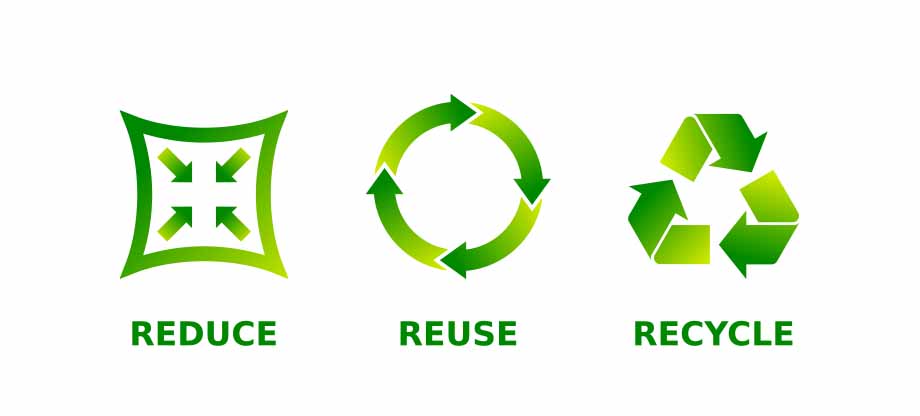
Both the 3 Rs and the 5 Rs include the steps Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle.
Reduce: Waste reduction starts with the product manufacturer and ends with the customer. While the manufacturer controls the materials and how the product is made and packaged. It is the customer’s responsibility to choose products with the least environmental impact. The best way to reduce waste is to not create it in the first place.
Reuse: This step involves taking an item and either using it again for its original purpose or finding it another purpose.
Recycle: This step is more complex compared to the first two. It involves taking an item through a manufacturing process so it can be used to create new materials and items.
The 5 Rs
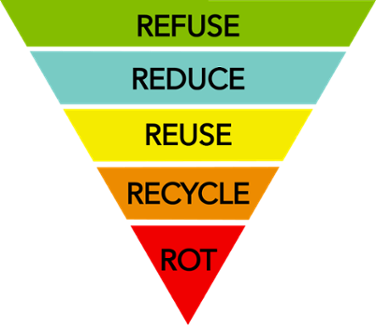
The 5 Rs extend beyond the more traditional 3 Rs model to include Refuse and Rot. Following the 5 Rs model results in less waste being created and greater waste diversion than the 3 Rs model.
Refuse: This step asks us to consider what we really need before we even begin to interact with a product. If we say no to things we don't need, we can decrease our waste before it is ever created.
Rot: Some of the waste we create, such as food scraps and garden waste, is organic waste that can be composted. Composting can be thought of as a natural form of recycling, in which the natural processes of rot return the nutrients in organic waste to the soil.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.

